Expert Care in Managing Osteoporosis & Metabolic Bone Disorders
The Utah Diabetes and Endocrinology Center at University of Utah Health has launched a bone health program that is unique to the region. The Osteoporosis and Metabolic Bone Health program is designed to provide comprehensive, single-window access to high-quality patient care in northern Utah.
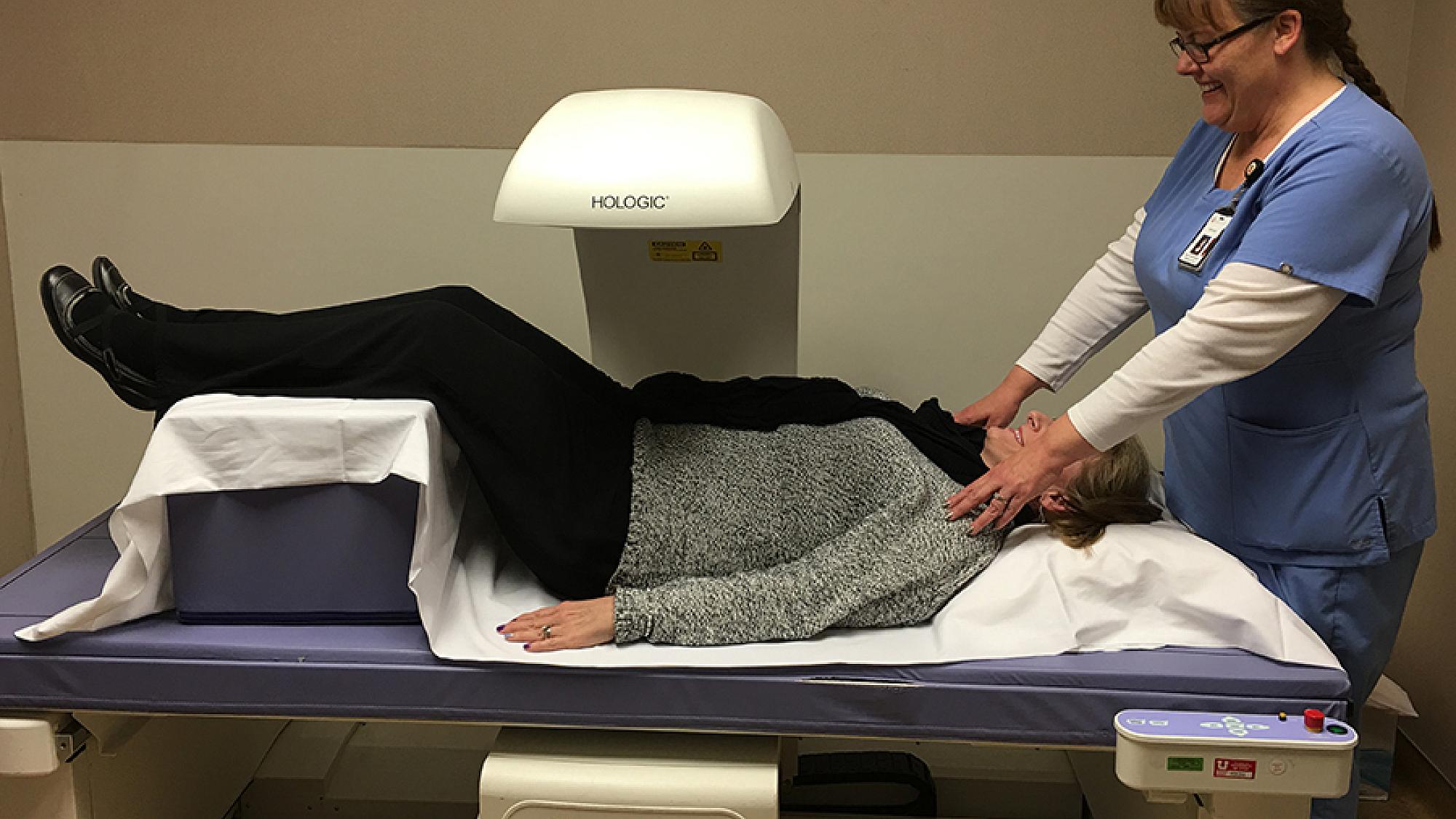
Our endocrinologists provide targeted, advanced care for women and men. Our state-of-the-art DEXA scans and infusion and lab services provide comprehensive, efficient care in one convenient location.
We engage in clinical trials and research to offer you the most leading-edge therapies. Recognized experts, including an ambassador for the National Bone Health and Osteoporosis Foundation, are part of our team. When you choose U of U Health, you are choosing an established, expert team.
Services & Treatments for Osteoporosis & Other Metabolic Bone Disorders
- Screening and diagnosis of osteoporosis and other metabolic bone disorders
- Evaluation for secondary causes of pathological bone loss such as thyroid, parathyroid, and adrenal disorders
- Same-day high-quality bone density scan (DXA) as available
- DXA reporting performed by a certified clinical densitometrist
- Fall risk assessment conducted by certified geriatrician or physical therapist
- Counseling on calcium and vitamin D intake by registered pharmacist
- Weight bearing and muscle strengthening exercises recommended by a certified physical therapist
- Medication therapy by a certified endocrinologist
- Biochemical markers of bone turnover to monitor treatment efficacy
- Follow-up of test results and management plan via telephone, secure email, or mail
Can Osteoporosis Be Reversed?
You can reverse osteoporosis with a combination of medications and lifestyle changes. It’s not possible to reverse osteoporosis with lifestyle changes alone. Your provider will explain your chances of reversing osteoporosis, depending on the severity of the condition.
What Doctor Treats Osteoporosis?
Your primary care provider will diagnose osteoporosis. They may treat you or refer you to a specialist such as an endocrinologist, a doctor specializing in hormone-related conditions.
Find an Endocrinology Specialist
Refer a Patient
To refer a patient to the Osteoporosis and Metabolic Bone Health Program, call 801-581-7761.
Patient Resources
Bone Density Scan
University of Utah Health offers bone density scans—also called DEXA scans—to measure how healthy your bones are.
Osteoporosis Resources
If you've just been diagnosed with osteoporosis, you may be wondering what that means for your health. The good news is that it can be diagnosed and treated.
Hear From Our Specialists
Support Your Bones & They'll Support You
You're never too young or too old to be concerned about bone health. If you don't consume enough calcium in your diet to keep your body functioning, calcium is depleted from your bones, your bone density is reduced, and the risk of breaking your bones is increased.
Keeping Your Bones Healthy & Strong Through the Years
Osteoporosis and other bone conditions can mean the difference between living independently and needing full-time assistance as we age. One of our women's health experts weighs in on what constitutes good bone health—and how you can help ensure your bones stay strong as you age.