What Is Skin Lupus?
Skin lupus, is an autoimmune skin disease that occurs when your immune system attacks healthy skin cells by mistake and damages your skin. This can cause redness, itching, pain and eventual scarring of the skin.
Lupus of the skin can occur by itself or manifest as a part of systemic lupus erythematosus — the most serious type of lupus that affects your entire body like your joints, kidneys, heart, lungs, blood vessels, and brain.
Cutaneous lupus, the type affecting the skin, can be effectively treated by our highly trained specialists at the autoimmune skin disease clinic for University of Utah Health.

Types of Skin Lupus
There are three kinds of cutaneous lupus, which include:
- Discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE) — This type causes a red rash that will not disappear and can leave scarring.
- Subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus (SCLE) — This kind will cause sores on parts of the skin that have been exposed to the sun like the upper trunk and arms.
- Acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus (ACLE) — This type may cause a rash on the upper cheeks and nose. It is often a sign of systemic lupus erythematosus.
While these are all different specifications of the disease, they often display similar symptoms.
What Causes Lupus?
The exact cause of lupus continues to leave the medical community perplexed. But doctors can say with certainty that lupus is not contagious so you cannot catch it from someone else. However, your genes can play a potential role in your risk for developing lupus. Researchers are currently studying the possible causes of lupus by looking at different hormones, immune system problems, and environmental and lifestyle factors such as sunlight exposure, smoking, stress, and more.
Find an Autoimmune Skin Disease Specialist
Skin Lupus Symptoms
The typical signs of lupus include, but are not limited to, the following symptoms:
- rashes,
- sores,
- hair loss, and
- sensitivity to the sun.
These symptoms may also be accompanied by:
- joint aches,
- headaches, and
- fatigue.
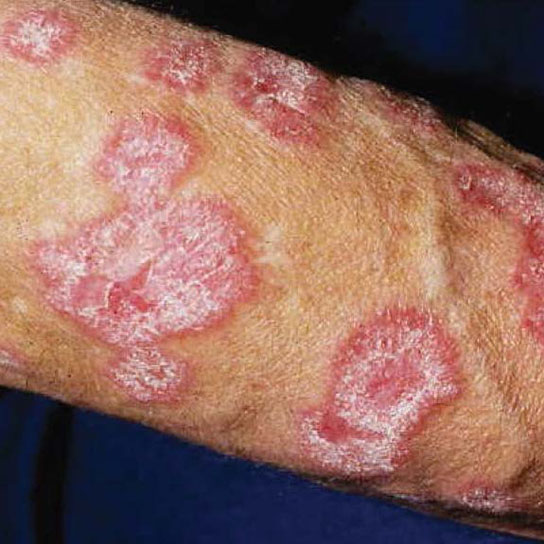

What Does a Lupus Rash Look Like?
A lupus rash can appear in the following ways:
- A scaly, butterfly-shaped rash that covers both your cheeks and the bridge of your nose, This rash will not leave any scarring in its wake, but you may notice some skin discoloration such as dark or light-colored areas.
- Red, ring-shaped lesions that do not itch or scar. They can appear on your arms, shoulders, neck or any body part that has been exposed to the sun. These lesions may discolor your skin over time.
- Red, scaly coin-shaped lesions that appear on your scalp and face. These do not hurt or itch, but they can scar your skin and discolor it. Your hair may fall out because these lesions can clog the hair follicle. Hair loss could become permanent if the lesions form scars when they heal.
- A rash in between the knuckles of the fingers.
How Do You Diagnose Lupus of the Skin?
Lupus is not easy to diagnose because the signs can vary from person to person. The symptoms can even overlap with other disorders, which could lead to a misdiagnosis. Plus, there is no test that can diagnose lupus.
For skin lupus, we often remove a small piece (biopsy) of the rash or lesion and inspect it under a microscope to see if it has any features of cutaneous lupus. If systemic lupus is suspected, we conduct blood and urine tests in addition to your physical examination to help diagnose you.
Lupus Rash Treatment
If you are diagnosed with lupus, our physicians may prescribe an oral medication such as an antimalarial. However, there are lifestyle changes you can make to ease the symptoms and prevent lupus flare-ups:
- avoid sun exposure,
- use sunscreen with an SPF of 70 or higher,
- wear protective clothing when outdoors,
- reduce stress, and
- stop smoking.
Skin Lupus Prognosis
Skin lupus varies in severity from person to person, so you should monitor your symptoms and follow the instructions given to you by your physician. A combination of medication and preventative lifestyle habits are typically successful in easing lupus symptoms affecting the skin.
Make An Appointment with Our Specialists
A referral is required to meet with an autoimmune skin disease specialist. However, if you have questions about a skin condition without a pre-existing diagnosis, you can schedule an appointment with a general dermatologist at the U of U Health clinic by contacting 801-581-2955.
For new patients with an existing diagnosis, you will need a referral from your current provider. Your referral should include your name, date of birth, home address, phone number, and insurance company.
Before your first appointment, records about your autoimmune history should be faxed to U of U Health at 801-581-4911. These records should include clinic notes, biopsy reports, lab reports, diagnostic studies, radiographic studies, and treatments.
Please make sure your doctor faxes your referral to:
University of Utah
Department of Dermatology
Attn: Autoimmune Clinic
Phone: 801-581-2955, ask for autoimmune scheduling
Fax: 801-581-4911
We will review referral requests within 48 hours to make sure that the best dermatologist evaluates each case. We will contact new patients about an appointment.

